Hello fellow brewing enthusiasts! Today, I’ll be sharing my experience and knowledge on a topic that may seem a bit technical but is actually quite fundamental to the brewing process: amylase. The question that we’re addressing is: how much amylase to use in brewing?
The general rule of thumb is to use 0.1 to 0.3 teaspoons of amylase per gallon of mash, depending on the specific type of amylase and the desired result.
However, this number can be adjusted based on the brewer’s personal preference and the specific conditions of the brew.
What is Amylase?
Before we delve into the nitty-gritty of how much amylase to use, it’s important to understand what amylase is and why it’s used in brewing.
Simply put, amylase is an enzyme that breaks down starches into sugars. These sugars are then fermented by the yeast to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide, which are the main components of beer.
Amylase is naturally present in grains, and the malting process is designed to activate these enzymes.
However, in certain situations, such as when using a large amount of un-malted grains or adjuncts, additional amylase may be needed to ensure a complete conversion of starches to fermentable sugars.
Why would you add amylase enzyme in beer brewing?
When to Add Amylase
Amylase should be added during the mashing process, as this is when the starches in the grain are most accessible. Depending on your brewing setup, you can either add it directly to the mash tun or mix it in with the grain before mashing.
Types of Amylase
There are two main types of amylase used in brewing: alpha-amylase and beta-amylase.
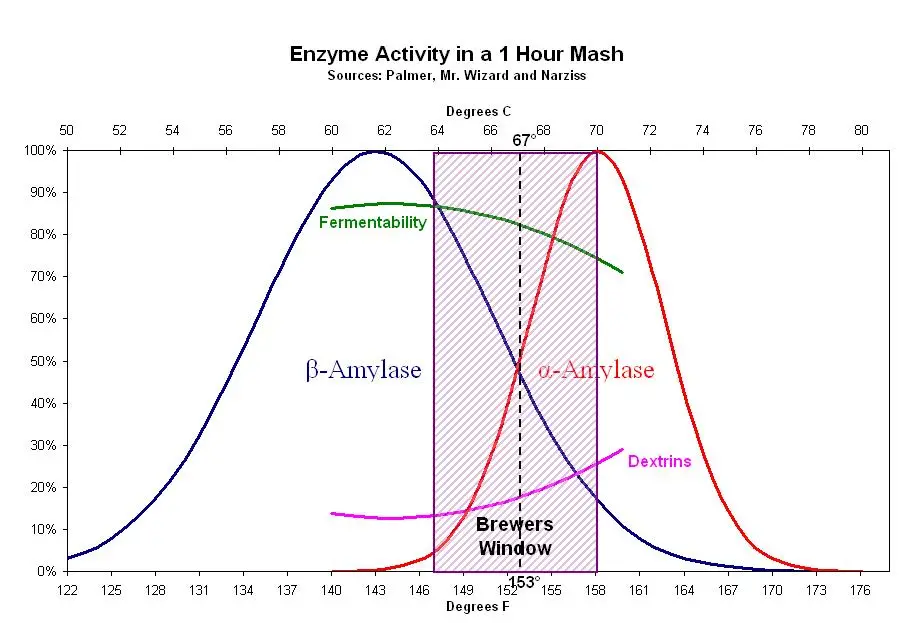
Alpha-Amylase
Alpha-amylase is the more aggressive of the two, breaking down starches into a mix of fermentable and unfermentable sugars. This results in a beer with a fuller body and higher alcohol content. It works best at a temperature range of 154-162°F (68-72°C).
Beta-Amylase
On the other hand, beta-amylase works by gradually chipping away at the ends of the starch molecules, producing primarily fermentable sugars. This leads to a beer with a lighter body and lower alcohol content but potentially higher carbonation. It operates best at a temperature range of 131-150°F (55-66°C).
Effects of Amylase on the Brew
The quantity of amylase used can directly affect the characteristics of your brew. More amylase will result in more sugar conversion, leading to a higher alcohol content and a drier, less sweet beer. Less amylase, on the other hand, can lead to a sweeter, full-bodied beer with a lower alcohol content.

Calculating the Amount of Amylase to Use
When it comes to determining how much amylase to use in brewing, it’s not an exact science, but rather a balance of art and science.
The amount of amylase to add depends on the type of grains or adjuncts you’re using, the desired alcohol content, and the overall character you want to achieve in your beer.
As previously mentioned, a common rule of thumb is to use 0.1 to 0.3 teaspoons of amylase per gallon of mash.
However, this can vary depending on the specific conditions of your brew.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, amylase is a powerful tool in the brewer’s arsenal, allowing for greater control over the flavor, body, and alcohol content of the beer. While the quantity of amylase to use can vary depending on various factors, a good starting point is 0.1 to 0.3 teaspoons per gallon of mash. As with all aspects of brewing, experimentation is key, so don’t be afraid to adjust the amount of amylase to suit your own tastes and brewing style.
Listicle of Facts:
1. Amylase is an enzyme that breaks down starches into sugars, which are fermented by yeast to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide.
2. There are two main types of amylase: alpha-amylase and beta-amylase.
3. Alpha-amylase is more aggressive, breaking down starches into a mix of fermentable and unfermentable sugars.
4. Beta-amylase produces primarily fermentable sugars, leading to a beer with a lighter body and potentially higher carbonation.
5. More amylase will result in more sugar conversion, leading to a higher alcohol content and a drier beer.
6. The rule of thumb is to use 0.1 to 0.3 teaspoons of amylase per gallon of mash.
7. The amount of amylase to add depends on the type of grains or adjuncts you’re using, the desired alcohol content, and the overall character you want to achieve in your beer.
8. Amylase should be added during the mashing process.
9. The use of amylase allows for greater control over the flavor, body, and alcohol content of the beer.
10. Experimentation is key in determining the right amount of amylase for your brew.
FAQs
How much amylase do I use?
The amount of amylase to use depends on the specific application or recipe you are using. It is typically recommended to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer or a trusted recipe source. The required quantity can vary based on factors such as the desired outcome, volume of the mixture, and the concentration of the amylase enzyme.
How do you use amylase enzyme in brewing?
Amylase enzyme is commonly used in brewing to break down starches into fermentable sugars. It is typically added during the mashing process, where it helps convert complex starches in malted grains into simpler sugars that yeast can consume and convert into alcohol. This enzyme helps improve the efficiency of the brewing process by increasing sugar extraction, resulting in better fermentation and flavor development.
What is the optimal substrate concentration for amylase?
The optimal substrate concentration for amylase can vary depending on the specific enzyme and experimental conditions. Generally, amylase activity tends to increase with increasing substrate concentration up to a certain point, after which the rate of reaction plateaus. This is because the active sites of the enzyme become saturated with substrate molecules. Therefore, it is important to determine the optimal substrate concentration for each specific amylase through experimentation to achieve the highest enzymatic activity.
How much liquid alpha amylase to use?
The amount of liquid alpha amylase to use depends on the specific application and the desired enzymatic activity. It is best to refer to the manufacturer’s instructions or consult with a technical expert to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs.
What is the role of amylase in beer?
Amylase plays a crucial role in beer production as it helps convert starches into fermentable sugars. This enzyme breaks down complex carbohydrates present in malted barley, allowing yeast to consume these sugars during fermentation. This process is essential for the production of alcohol and carbon dioxide, contributing to the flavor, aroma, and overall quality of the beer.
How much amylase to use in bread?
The amount of amylase to use in bread depends on various factors such as the desired texture, dough consistency, and the specific amylase enzyme being used. It is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s instructions or consult a recipe that specifically calls for amylase to ensure the appropriate amount is used.




-recipe.jpg)