As a passionate and experienced brewer, I often get asked the question, “How long does it take for fermentation to start?”
This is a critical aspect of the brewing process and one that can significantly impact the quality of your final product.
The fermentation process starts almost as soon as the yeasts is rehydrated and has access to sugar and the oxygen in the fermentation tanks i depleted. The actual physical signs of fermenation (bubbles, foams, smells etc.) will usually start anywhere between 12 to 72 hours after you pitch your yeast.
However, this timeframe can vary significantly depending on various factors, which we’ll delve into deeper in this article.
Understanding Fermentation
Before diving into the specifics of the fermentation timeline, it’s important to understand what fermentation is.
Fermentation is the metabolic process that yeast undergoes to convert sugar into alcohol and carbon dioxide.
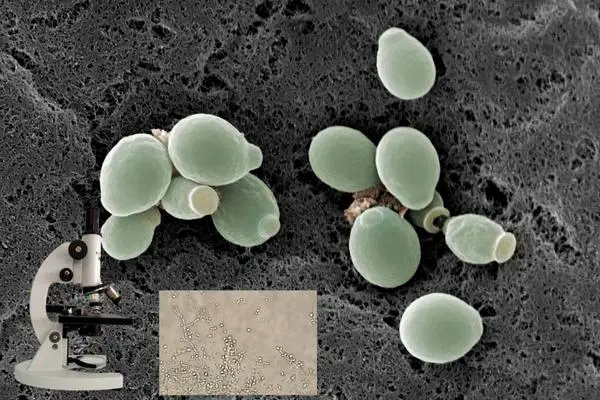

This process is what transforms a simple brew into an enjoyable beer, wine or any other fermented beverage.
The fermentation process begins when yeast is introduced into a sugar-rich environment, like a brewing wort or a grape must.
The yeast cells consume the sugar, producing carbon dioxide in return, and heat as as by-products.
This initial part of yeast metabolism is not fermentation but simply respiration as we humans do it. This is because oxygen is still present in the fermenter, and it needs to be used first before the actual fermentation can begin.
Yeast greatly prefer to use the oxygen first, so it will only really start to ferment when all oxygen is gone.
Then it uses the sugars to ferment (donate electrons to) as it used oxygen before, but as it cannot fully break down the sugar, it ends up as ethanol instead of pure CO2.
The yeast will ferment as long as the air in the fermenter is oxygen-free, if you open the lid too much during fermentation, it will slow down alcohol production and risk contamination.
This fascinating process is what gives our favorite drinks their unique flavors and body.
The Role of Yeast
When we talk about fermentation, we cannot overlook the role of yeast. Yeast is a key player in the fermentation process. The type of yeast you choose can greatly affect the fermentation time and the flavor profile of your brew.
Different strains of yeast have different sugar consumption rates, alcohol tolerances, and flavor profiles. For example, ale yeasts (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) tend to ferment faster and at higher temperatures, while lager yeasts (Saccharomyces pastorianus) ferment slower and at lower temperatures.
Factors Influencing Fermentation Start Time
Fermentation start time is influenced by a multitude of factors, each with its unique role in the brewing process. Let’s delve deeper into each factor, discussing their importance and how they influence the start of fermentation.
1. Yeast Health:
Yeast cells need to be in good condition to perform their metabolic functions effectively. Healthy yeast means cells are fresh, active, and free from any contaminants. Old or stressed yeast might not be as efficient in starting the fermentation process.
2. Wort Temperature:
Every yeast strain has an optimal temperature range for fermentation. Pitching yeast into wort that’s within this range ensures a faster start. Wort that’s too cold can make yeast dormant, while too hot wort can kill the yeast.
3. Oxygen Levels:
Yeast requires oxygen during the initial phases for cell growth and multiplication. Insufficient oxygen can hinder this, delaying the fermentation start. Conversely, too much oxygen post fermentation can spoil the beer.
4. Sugar Content (Original Gravity of Wort):
High gravity worts (those with more sugar) can sometimes delay the start of fermentation. This is because they create a more stressful environment for the yeast due to osmotic pressure. The yeast might require more time to adapt before fermentation begins.
5. Pitching Rate:
The amount of yeast pitched into the wort can influence the fermentation start time. Insufficient yeast can lead to a delayed onset of fermentation, while over-pitching may result in a faster, but sometimes undesirable fermentation character.
6. Wort pH:
The acidity or alkalinity of wort can impact yeast activity. Most yeast strains prefer a pH range of 4.0 to 5.5. Wort outside this range can stress the yeast, affecting the fermentation start.
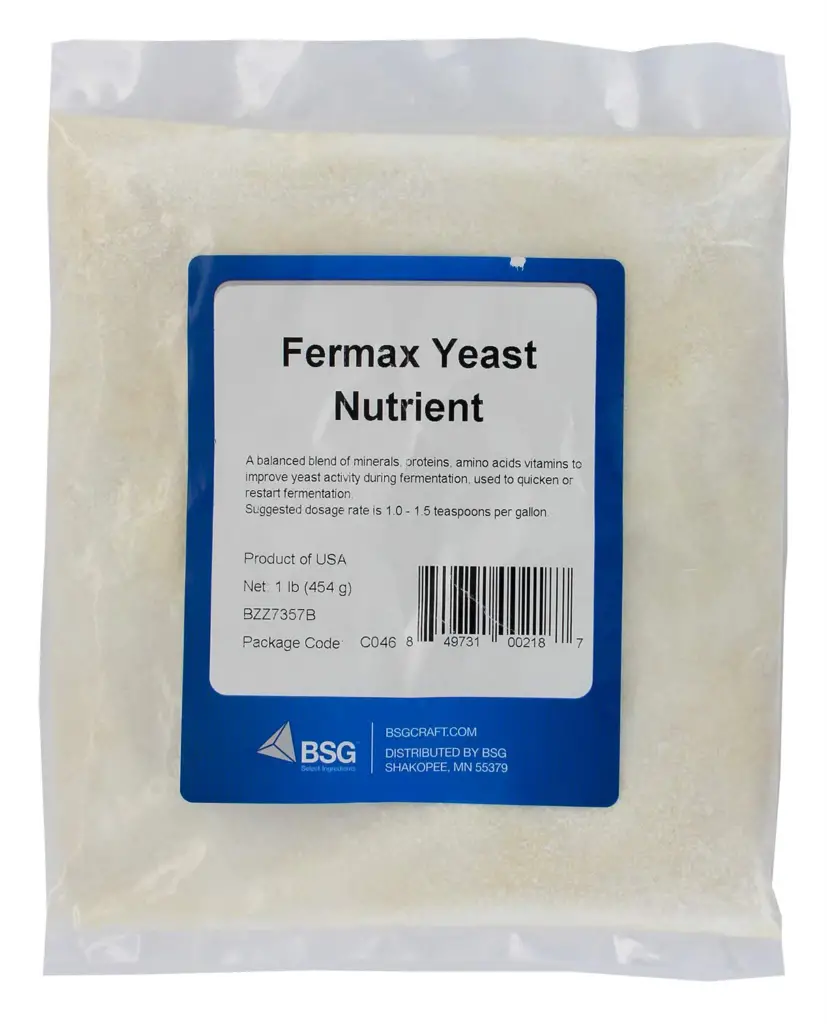
7. Nutrient Availability:
Yeast requires essential nutrients like nitrogen, vitamins, and minerals for healthy fermentation. A deficiency in these nutrients can delay the start and even lead to incomplete fermentation.
Fermax Yeast Nutrients
8. Presence of Inhibitors:
Certain compounds like preservatives or high alcohol levels can inhibit yeast activity. If the wort has any inhibitors, they can delay or even halt fermentation.
9. Strain Variation:
As mentioned, different yeast strains have different metabolic rates and optimal conditions. Thus, the strain you choose can influence how quickly fermentation starts.
10. Previous Yeast Handling:
How the yeast was handled before pitching, including storage conditions, rehydration methods (if using dry yeast), and propagation methods, can also influence its health and vigor.
Table Ranking the Factors by Influence on Fermentation Start Time:
| Rank | Factor | Influence on Fermentation Start Time |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yeast Health | High |
| 2 | Wort Temperature | High |
| 3 | Oxygen Levels | High |
| 4 | Sugar Content | High |
| 5 | Pitching Rate | Moderate |
| 6 | Wort pH | Moderate |
| 7 | Nutrient Availability | Moderate |
| 8 | Presence of Inhibitors | Moderate |
| 9 | Strain Variation | Moderate |
| 10 | Previous Yeast Handling | Low |
By understanding the influence of each factor on fermentation start time, brewers can better control their brewing process, leading to more consistent results and higher quality brews.
Recognizing the Start of Fermentation
Recognizing the start of fermentation is crucial for brewers. The signs of fermentation can be quite subtle, and if you’re not paying attention, you might miss them.
The first sign of fermentation is usually a frothy layer on top of the wort, known as the krausen.
This is followed by the release of carbon dioxide, which can be seen as bubbles in the airlock of your fermenter. You might also notice a change in the color and clarity of the wort as the yeast cells multiply and start doing their work.
Managing the Fermentation Process
Once fermentation has started, it’s critical to manage the process to ensure a successful brew. This involves maintaining the right temperature, racking the brew at the appropriate times, and knowing when to bottle your brew.
Maintaining the right temperature is key to a successful fermentation. Too high a temperature can cause off-flavors, while too low a temperature can cause the yeast to become dormant and stop fermenting.
Troubleshooting Fermentation Issues
Sometimes, despite your best efforts, fermentation might not start as expected. When this happens, it’s important to troubleshoot the issue and take corrective measures.
If fermentation hasn’t started within 72 hours, it’s likely that there’s an issue with the yeast. This could be due to insufficient yeast, unhealthy yeast, or yeast that’s been pitched at the wrong temperature. You might need to re-pitch with fresh, healthy yeast to get the fermentation going.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the start of fermentation can range anywhere between 12 to 72 hours after pitching your yeast. However, this timeframe can be influenced by various factors, including yeast health, wort temperature, oxygen levels, and sugar content. Recognizing the signs of fermentation, managing the process, and troubleshooting any issues are all crucial skills for brewers.
10 Key Facts About Fermentation:
1. Fermentation is the process of yeast converting sugar into alcohol and carbon dioxide.
2. The fermentation process can start anywhere between 12 to 72 hours after you pitch your yeast.
3. The type of yeast used can greatly affect the fermentation time and the flavor profile of the brew.
4. Healthy yeast will start the fermentation process more quickly than stressed or old yeast.
5. Wort temperatures within the yeast’s preferred range will encourage faster fermentation starts.
6. The first sign of fermentation is usually a frothy layer on top of the wort, known as the krausen.
7. Maintaining the right temperature is key to a successful fermentation.
8. If fermentation hasn’t started within 72 hours, it’s likely that there’s an issue with the yeast.
9. Re-pitching with fresh, healthy yeast can help to kickstart the fermentation process.
10. Understanding and managing the fermentation process is an essential skill for brewers.
In my personal experience, understanding the fermentation process has been key to creating high-quality brews. It’s a fascinating process, and there’s always something new to learn. So keep brewing, keep learning, and most importantly, keep enjoying the fruits (or brews) of your labor!
FAQs
How long does it take for yeast to start bubbling?
Typically, it takes around 30 minutes to 2 hours for yeast to start bubbling and showing signs of fermentation.
How long does fermentation take to start?
Fermentation typically begins within a few hours to a couple of days, depending on the specific type of fermentation and the conditions provided.
How long does fermentation usually take?
Fermentation usually takes a few days to a few weeks, depending on the specific type of fermentation and the conditions in which it is carried out.
Can fermentation be done in 2 days?
Yes, fermentation can be done in 2 days.
What is the minimum time to ferment beer?
The minimum time required to ferment beer typically ranges from one to two weeks, depending on the specific beer style and fermentation conditions.
How long does it take to ferment?
The time it takes for fermentation to occur can vary depending on the specific process and ingredients involved. It can range from a few hours to several weeks.





