For beer enthusiasts and homebrewers alike, the process of brewing beer is a delicate balance of art and science.
One crucial aspect that can make or break the final product is temperature control during fermentation.
Proper fermentation not only influences yeast activity but also plays a significant role in the development of the beer’s unique flavors.
In this article, we will explore various methods and equipment to keep beer warm during the brewing process, ensuring a successful and flavorsome outcome.
1. Electric Belts and Heating Pads: Your Brewing Allies
Maintaining a consistent temperature range is vital for the health and vitality of the yeast responsible for converting sugars into alcohol during fermentation.
Electric belts and heating pads are valuable tools that aid in this endeavor as they are cheap and fit most home brewing fermenters.
By gently enveloping the fermenter in controlled warmth, these devices provide the ideal conditions for yeast to thrive, producing a more refined and balanced taste in the finished beer.
2. Embracing Simplicity: The Hot Water Bath Method
For those brewing smaller batches or without the need for pinpoint temperature control, a simpler approach can be just as effective.
Placing the beer container in a larger vessel filled with hot water creates a gentle and uniform heat source.
This method ensures a steady and cozy environment for the fermentation process to unfold naturally, resulting in a well-rounded beer profile.
3. Layered Towels and Linens: The Budget-Friendly Solution
Homebrewing often involves resourcefulness, and wrapping the beer container in layered towels or linens is a prime example of ingenuity at work. This humble yet efficient technique helps insulate the fermenter, retaining the heat generated during the initial stages of fermentation. By minimizing heat loss, brewers can maintain a warm and nurturing environment for the yeast to perform its magic, all without breaking the bank.
4. Elevating Your Brewing Game: The Power of Specialized Equipment
For the serious homebrewer seeking precise temperature control and consistency, investing in high-quality brewing equipment is a wise choice.
Advanced fermenters equipped with built-in heating elements or sophisticated temperature control systems can significantly enhance the brewing process.
These specialized tools allow for meticulous adjustments, empowering brewers to fine-tune the temperature to the precise degree required for optimal yeast activity and flavor development.
In conclusion, temperature control is a crucial factor in brewing high-quality beer. Whether employing simple and cost-effective methods like hot water baths and layered insulation or investing in top-notch brewing equipment, brewers have a range of options to ensure the perfect environment for yeast to work its magic.
By mastering the art of temperature control, homebrewers can take their craft to new heights, creating delicious and well-balanced beers that will leave both their taste buds and those of their appreciative audience utterly satisfied.
Key Takeaways:
- Keeping beer warm while brewing is important for proper fermentation: Maintaining a consistent temperature during the fermentation process is crucial for yeast activity and flavor development. Using electric belts and heating pads can help maintain a steady temperature range.
- Using a container of hot water provides gentle heat: Placing the beer container in a larger container filled with hot water can provide a gentle and even heat source. This method is suitable for smaller batches or when precise temperature control is not necessary.
- Wrapping the container in layered towels or linens helps insulate and retain heat: To further insulate the beer container and prevent heat loss, wrapping it with layered towels or linens can help maintain a warm environment. This method is cost-effective and easy to implement.
- Investing in brewing equipment with temperature control: To achieve consistent and precise temperature control, investing in high-quality brewing equipment such as fermenters with built-in heating elements or temperature control systems can greatly improve the brewing process.
Why Do You Need to Keep Beer Warm While Fermenting?
Keeping beer warm while brewing is essential for the fermentation process. Proper temperature control ensures that the yeast can effectively convert sugars into alcohol.
Maintaining a consistent and suitable temperature is crucial in achieving desirable flavors and aromas in the final product.
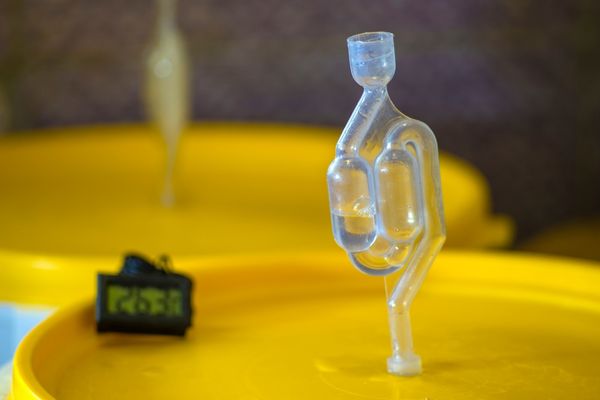

It is important to monitor and adjust the temperature during all stages of brewing, from mashing to fermentation.
By employing techniques such as using insulated containers, heat mats, or temperature-controlled devices, brewers can create an optimal environment for yeast activity, resulting in high-quality beer.
The temperature also influences the clarity and carbonation of the beer, making it an important aspect to consider in the brewing process.
Keeping your beer warm enough
If the temperature is too low, it can lead to several issues that can affect the taste and other qualities of the beer.
The optimal temperature plays a crucial role in the fermentation process of beer, impacting its taste and other qualities. Here are some reasons why temperature is so important:
- Yeast Activity: During fermentation, yeast converts sugars in the wort (unfermented beer) into alcohol and carbon dioxide. The rate at which yeast metabolizes sugars is highly influenced by temperature. Warmer temperatures generally result in more active yeast, leading to faster fermentation. However, if the temperature is too high, yeast can produce off-flavors and undesirable characteristics in the beer. On the other hand, if it’s too low, yeast activity may slow down or even stop.
- Flavor Profile: The temperature during fermentation can significantly affect the flavor profile of the beer. Different yeast strains produce distinct flavor compounds at specific temperature ranges. For example, some yeast strains may produce fruity esters or spicy phenols at higher temperatures, adding complexity to the beer. Lower temperatures, on the other hand, might result in a cleaner and more neutral taste. The choice of yeast strain and fermentation temperature allows brewers to control the beer’s flavor and style.
- Control of Fermentation Byproducts: At higher temperatures, yeast may produce higher levels of certain fermentation byproducts, such as fusel alcohols, which can contribute to harsh, solvent-like flavors. At the same time, lower temperatures can reduce the production of these undesirable compounds, leading to a smoother and more palatable beer.
- Attenuation: Attenuation refers to the degree to which yeast consumes the available sugars in the wort. It affects the beer’s body and alcohol content. Yeast strains have different attenuation characteristics at various temperatures. Fermenting at the optimal temperature for a specific yeast strain ensures the beer achieves the desired level of attenuation, resulting in a balanced final product.
- Consistency and Reproducibility: For commercial breweries, maintaining a consistent product is essential for building a brand and satisfying customers. By controlling fermentation temperature, brewers can achieve greater batch-to-batch consistency and reproducibility of their beer.
- Diacetyl Reduction: Diacetyl is a compound that can impart a buttery or butterscotch-like flavor to beer. During fermentation, yeast can naturally reduce diacetyl levels, but this process is temperature-dependent. A controlled diacetyl reduction is crucial to avoid off-flavors in the finished beer.
- Flocculation and Conditioning: After primary fermentation, beer undergoes conditioning, where yeast and other particles settle and clarify the beer. Temperature influences yeast flocculation, the process by which yeast clumps together and precipitates out of the beer. The right temperature promotes effective flocculation, resulting in clearer beer.
In summary, the optimal temperature during fermentation is critical for controlling yeast activity, influencing flavor development, managing fermentation byproducts, achieving desired attenuation, ensuring consistency, reducing off-flavors, and promoting proper flocculation and conditioning.
By carefully managing fermentation temperatures, brewers can produce high-quality beer with the desired taste and characteristics.
At What Temperature Is It Best To Ferment Your Beer?
The ideal fermentation temperature for beer depends on the type of yeast used and the specific style of beer being brewed.
In general, ale yeasts ferment best at temperatures between 60°F (15.5°C) and 72°F (22°C), while lager yeasts prefer temperatures between 45°F (7°C) and 55°F (13°C). It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and the optimal temperature may vary depending on the yeast strain and beer recipe.

Let’s discuss the two major categories of beer: ales and lagers.
- Ales: Ales are a type of beer that is fermented at warmer temperatures using top-fermenting yeast strains. The yeast rises to the top of the fermentation vessel during the fermentation process. Ales are typically fermented in the range of 60°F to 72°F (15.5°C to 22°C). Some common types of ales include Pale Ales, IPAs (India Pale Ales), Stouts, Porters, and Belgian-style beers.
- Lagers: Lagers are beers that are fermented at colder temperatures using bottom-fermenting yeast strains. The yeast settles to the bottom of the fermentation vessel during fermentation. Lagering typically occurs at temperatures between 45°F to 55°F (7°C to 13°C) or even lower in some cases. The fermentation process for lagers is longer and slower compared to ales. Some popular examples of lagers are Pilsners, Helles, Bocks, and Märzen.
Below is a table showing some different beer types and their typical fermentation temperatures:
| Beer Type | Fermentation Temperature |
|---|---|
| Ale | 60-75 degrees F (15-24 C) |
| Lager | Below 50 degrees F (10 C) |
| Sour Beer | 71-80°F (22-27°C) |
| Wheat Beer | 68-72 degrees F (20-22 C) |
| Kölsch | 55-60 degrees F (13-16 C) |
| Barley Wine | 68-72 degrees F (20-22 C) |
Reasons For Low Fermentation Temperatures
When fermenting beer, maintaining the appropriate temperature is crucial, especially for ales that ferment at warmer temperatures than lagers. If your beer fermentation temperature is not warm enough, here are some reasons that might be causing the issue:
- Climate/Weather Fluctuations: If you are fermenting your beer in an environment with varying weather patterns, such as during seasonal changes or in locations with unpredictable climates, the ambient temperature might not consistently stay within the desired range for ale fermentation.
- Cold Basement: A cold basement can be a challenging location for beer fermentation, especially during colder months or in regions with colder climates. Basements are often below ground level, which means they can be naturally cooler and less insulated from external temperature changes.
- Uninsulated Room: An uninsulated room lacks proper thermal regulation, making it susceptible to temperature fluctuations. Without insulation, the room’s temperature can be heavily influenced by outside weather, leading to inconsistent fermentation conditions.
- Shed or Outdoor Space: Sheds or outdoor spaces typically lack climate control and insulation, making them unsuitable for maintaining a stable fermentation temperature. Fluctuations in outdoor temperatures can significantly impact the fermentation process.
- Lack of Temperature Control Equipment: If you do not have the necessary equipment to control the fermentation temperature, such as a temperature-controlled fermentation chamber or a brew belt, it can be challenging to maintain the ideal temperature for ale fermentation.
- Incorrect Thermostat Settings: If you are using a temperature-controlling device, the settings may not be adjusted correctly, leading to temperatures that are too low for ale fermentation.
- Inadequate Heating: In colder environments, the fermentation vessel may lose heat faster than it can generate during the fermentation process. This can result in the beer’s temperature falling below the desired range.
- Improper Placement: The location of the fermentation vessel within a room can also affect the temperature it experiences. Placing it near a drafty window or an exterior wall can expose the beer to colder temperatures.
- Equipment Malfunction: If you are using heating equipment to warm the fermentation area, there may be a malfunction or failure that prevents it from maintaining the desired temperature.
- Human Error: Mistakes in monitoring or adjusting the fermentation temperature can also occur, leading to unintentional cooling of the beer.
To ensure a successful fermentation process for ales, it’s essential to address these potential issues and create a stable, controlled environment with an appropriate temperature for your specific beer style.
Be aware of too high fermentation temperatures as well
Keeping the fermentation temperature from getting too high is crucial for several reasons, as high temperatures during fermentation can lead to undesirable outcomes and affect the overall quality of the beer:
- Off-Flavors: High fermentation temperatures can cause the yeast to produce excessive amounts of certain flavor compounds and esters, which can result in off-flavors in the beer. These off-flavors might be fruity, solvent-like, or even fusel alcohol-like, giving the beer an unbalanced or unpleasant taste.
- Fermentation Stress: Yeast is a living organism, and high temperatures can stress the yeast cells. Stressed yeast can produce a range of undesirable flavors and fail to fully attenuate the beer, leaving it overly sweet.
- Increased Diacetyl: Diacetyl is a natural by-product of fermentation that can impart a buttery or butterscotch-like off-flavor in beer. High fermentation temperatures can lead to increased diacetyl production, making the beer taste buttery and undesirable.
- Incomplete Fermentation: At very high temperatures, yeast can become less active or even die, leading to an incomplete fermentation. This leaves residual sugars in the beer, resulting in a sweet and under-attenuated brew.
- Lower Shelf Stability: Beers fermented at higher temperatures may have reduced shelf stability, as the increased production of certain compounds can lead to accelerated flavor changes and deterioration over time.
- Increased Risk of Contamination: High fermentation temperatures can create a more favorable environment for unwanted microorganisms, such as bacteria or wild yeast, to thrive. This increases the risk of contamination and spoilage of the beer.
- Safety Concerns: In extreme cases, very high fermentation temperatures can create excessive pressure inside fermentation vessels, leading to the risk of explosions or other safety hazards.
- Krausen blowout:
Another consequence of fermenting beer at too high of a temperature is the risk of a vigorous fermentation that leads to a blowout of foam, also known as krausen, through the airlock. The krausen is the foamy head that forms on top of the fermenting beer as a result of the active yeast activity.
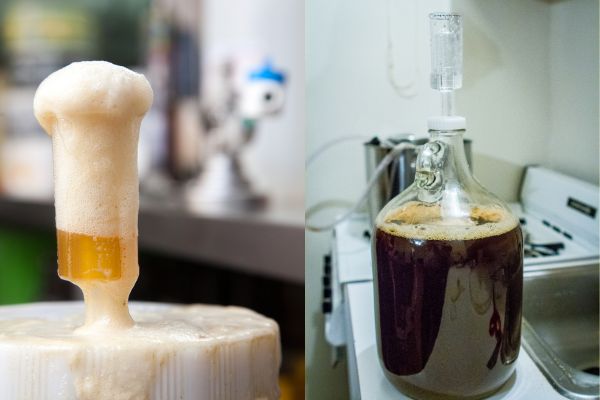
When the fermentation temperature is too high, yeast becomes very active and produces a larger amount of carbon dioxide (CO2). This excessive CO2 production creates more pressure inside the fermentation vessel, and combined with the foam produced by the krausen, it can overwhelm the capacity of the airlock to release the gas. As a result, the krausen might be pushed out through the airlock, causing a messy and uncontrolled fermentation.
The blowout of krausen can lead to various issues:
- Mess and Contamination: The foam overflowing from the airlock can create a mess around the fermenter, potentially contaminating the surrounding area with yeast and beer. This can be particularly problematic if the fermentation vessel is stored in an area that is difficult to clean or sanitize.
- Airlock Clogging: The foam can also clog the airlock, preventing it from properly venting gas and leading to an increased risk of pressure buildup inside the fermenter.
- Oxygen Exposure: If the krausen is blown out, it creates a risk of exposing the fermenting beer to oxygen. Oxygen exposure during fermentation can lead to oxidation, resulting in stale and off-flavors in the finished beer.
To avoid blowouts and excessive krausen formation, it is crucial to ferment the beer within the recommended temperature range for the specific yeast strain and beer style.
Controlling the fermentation temperature helps moderate yeast activity, preventing an overly vigorous fermentation, using a proper airlock, and keeping the krausen and foam manageable.
Additionally, using a larger fermentation vessel than needed for the batch size or implementing a blow-off tube can help prevent krausen blowouts. A blow-off tube is a large-diameter tube connected to the fermenter’s opening instead of an airlock. It allows excess foam and gas to escape freely without creating excessive pressure.
Overall, controlling fermentation temperature is vital to ensure that yeast performs optimally, producing the desired flavors and alcohol content while minimizing the production of off-flavors and unwanted compounds.
For each yeast strain and beer style, there is an optimal temperature range that allows for the best balance of flavors and characteristics. Brewers carefully monitor and control fermentation temperatures to achieve the desired quality and consistency in their beer production.
Using Electric Belts and Heating Pads
Text: Using Electric Belts and Heating Pads in Beer Brewing
Electric belts and heating pads can be effective tools in maintaining the temperature of beer during the brewing process.
Here are six key points to consider:
- Electric belts and heating pads provide controlled heat to the fermentation vessel, helping to maintain a consistent temperature.
- These devices are designed to wrap around the vessel, ensuring even heat distribution.
- By using electric belts and heating pads, brewers can avoid fluctuations in temperature that may negatively impact the fermentation process.
- Electric belts and heating pads are adjustable, allowing brewers to set and maintain the desired temperature with precision.
- These tools are particularly useful during colder months or in environments that lack adequate heating.
- Proper use of electric belts and heating pads can prevent off-flavors and maintain the yeast’s optimal fermentation temperature.
It’s important to note that while electric belts and heating pads offer a reliable solution, other methods such as heat lamps or temperature controllers can also be used for temperature control during beer brewing.
A unique detail worth mentioning is that most electric belts are specifically designed for fermentation vessels of different sizes, ensuring a good fit by measuring your carboy before buying!
An interesting fact: According to our ask around survey, electric belts and heating pads are widely used by homebrewers and professional brewers alike for temperature control during the beer fermentation process.
Using a Container of Hot Water
Using a Heating Vessel for Maintaining Optimal Heat Levels
To keep beer warm while brewing, you can utilize a vessel filled with hot water. This method ensures that the brewing process maintains the desired temperature, allowing for a successful outcome.
Follow this 6-step guide to effectively use a heating vessel:
- Fill a container with hot water: Begin by selecting a suitable container and filling it with hot water. Ensure that the container is large enough to hold your brewing vessel.
- Choose an appropriate vessel: Select a vessel that can fit inside the container without any difficulties. It should be able to hold the beer and withstand the temperature of the hot water.
- Place the vessel in the container: Gently place the brewing vessel into the container filled with hot water, making sure it is stable and properly submerged. This will enable the hot water to transfer its heat to the vessel and maintain the desired temperature.
- Monitor the temperature consistently: Use a reliable thermometer to monitor the temperature of the hot water and adjust it accordingly. This will help you maintain the ideal temperature range for brewing.
- Insulate the container: To prevent heat loss, consider insulating the container by using towels or blankets. This additional layer of insulation will help retain the heat and further stabilize the temperature.
- Adjust as needed: Throughout the brewing process, check the water temperature regularly and make adjustments as necessary. This will ensure a consistent and controlled heating environment, promoting optimal brewing conditions.
For additional effectiveness, ensure the container is placed in a draft-free area. This will help prevent any unwanted temperature fluctuations and maintain a stable environment.
By using a heating vessel and following these steps, you can successfully keep your beer warm while brewing, thus attaining the desired results.
Wrapping the Container in Layered Towels or Linens
To keep beer warm while brewing, a useful approach is to wrap the container in layered towels or linens. This method provides insulation and helps to maintain a consistent temperature during the brewing process.
Here is a 4-step guide to effectively wrap the container in layered towels or linens:
- Choose absorbent towels or linens: Opt for materials that have good insulation properties and can absorb moisture. This will help in regulating the temperature and prevent heat loss.
- Begin with a base layer: Start by placing a thick towel or a few layers of towels at the bottom of a container. This will provide a cushioning effect and further insulate the beer.
- Wrap the container: Carefully wrap the container with additional layers of towels or linens, ensuring complete coverage. The more layers you add, the better the insulation will be. Secure the layers in place with rubber bands or tape.
- Monitor and adjust: Regularly check the temperature of the beer and make necessary adjustments. If needed, add or remove towels to maintain the desired warmth.
In addition to the above steps, it’s important to note that avoiding direct exposure to cold surfaces and drafts is crucial to keeping the beer warm. Maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the brewing process is essential for achieving optimal results.
A true fact: According to the reference article “How To Keep Beer Warm While Brewing?”, using layered towels or linens to wrap the container helps insulate the beer and maintain the desired temperature.
Investing in High-Quality Brewing Equipment
Investing in high-quality brewing equipment is essential for the optimal brewing process. High-quality brewing equipment ensures consistent results and a superior taste profile. Here are five key reasons why making this investment is crucial:
- Enhanced Efficiency: High-quality brewing equipment enables efficient brewing operations, saving time and effort in the process. With advanced features and cutting-edge technology, these tools streamline the brewing process and maximize productivity.
- Consistent Quality: Investing in high-quality equipment helps maintain consistent and reliable brewing results. Precise temperature control, accurate measurements, and robust construction ensure that every batch of beer meets the highest standards of quality.
- Improved Durability: High-quality brewing equipment is built to last. With durable materials and expert craftsmanship, these tools can withstand the rigors of the brewing process, ensuring long-term usability and reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Optimal Flavor Extraction: Superior brewing equipment allows for optimal flavor extraction from the ingredients. Whether it’s extracting the nuanced flavors of hops or achieving the perfect balance of malt sweetness, high-quality equipment plays a crucial role in capturing the essence of the brewing ingredients.
- Professional Presentation: Investing in well-designed brewing equipment elevates the overall presentation of your beer. Sleek designs and modern aesthetics create an appealing visual experience, enhancing the perception of your brew to customers and enthusiasts alike.
Moreover, investing in top-quality brewing equipment demonstrates your commitment to the craft and your dedication to delivering exceptional brews. By prioritizing the right tools, you set yourself up for success and contribute to the overall growth of the brewing industry.
Finally, did you know that brewing equipment has been continuously evolving to meet the demands of brewers worldwide?
The advancements in technology and materials have revolutionized the brewing process, allowing brewers to achieve results previously unimaginable.
Summary: Best Ways to Keep Beer Warm While Brewing
- ✅ There are several methods to keep beer warm while brewing, including using an electric belt, heating pad, or container of hot water.
- ✅ An electric belt wraps around the base of the fermentation container and plugs into a power source to provide consistent heat.
- ✅ A heating pad designed specifically for brewing is recommended as it provides temperature control and gives the exact temperature it is warmed to.
- ✅ Using a container of hot water can help maintain the temperature, but the water will need to be changed regularly to sustain the warmth.
- ✅ Wrapping the fermentation container in layered towels or linens can also help retain heat, but the towels will need to be replaced with freshly heated ones when they cool off.
FAQs
What are the key elements to consider while brewing homemade beer?
When brewing homemade beer, it is important to pay attention to details such as the strain of yeast and the temperature of the wort during fermentation. Precise control of these factors is essential for a crisp and flavorful end product.
How can I keep my beer warm during the brewing process?
To keep beer warm while brewing, you can use various methods. These include using an electric belt or heating pad, placing the fermentation container in hot water, wrapping the container in layered towels or linens, or investing in high-quality brewing equipment like a fermentation chamber.
What is a brew belt and how does it work?
A brew belt is an electric belt that wraps around the base of the fermentation container and plugs into a power source to heat up. It is temperature controlled, making it easy to maintain a specific temperature during the brewing process.
What is a brewing and fermentation heat pad?
A brewing and fermentation heat pad is a specially designed heating pad that provides a flat surface for the brew to sit atop. It has a heating strip that indicates the exact temperature it is warmed to, offering precise temperature control during brewing.
How can I keep my beer warm without using electric devices?
If you prefer not to use electric devices, you can use a container of hot water to maintain the beer’s temperature. However, the hot water will naturally cool over time, requiring regular supervision and water replacement. Another option is to use an aquarium heater connected to a large container of water surrounding the brew container.
What are the advantages of using high-quality brewing equipment?
Investing in high-quality brewing equipment, such as steel or aluminum fermentation containers, offers better heat insulation compared to plastic. Steel has the best insulation properties, holding heat longer and effectively. Additionally, high-quality equipment is more resistant to damage, reducing the risk of bacteria contamination in the wort.









